For instance, Ford Motor Company has reduced the price of F-150 Lightning, its electric car, by $10,000. The company has been able to do so by consistently working on improving the efficiency of production and lowering manufacturing costs. For that purpose, the company used sensors to collect and analyze the cost of materials in real time to see how to optimize the costs. Manufacturing and non-manufacturing costs together form total costs for a manufacturing entity.
Cost types included
Whether you’re just starting your own manufacturing business or are looking to venture into the field of cost accounting, understanding manufacturing costs and knowing how to accurately calculate them is crucial for success. A manufacturing entity incurs a plethora of costs while running its business. While manufacturing or production costs are the core costs for a manufacturing entity, the other costs are also just as important as they too affect overall profitability.
Benefit #3: Assess the profitability of a product
Table 1.2 provides several examples of manufacturing costs at Custom Furniture Company by category. Fluctuation of costs is yet another challenge that makes it harder to calculate manufacturing costs accurately, according to Fabrizi. Next, calculate the value of the existing inventory if the manufacturing company already has a stock of materials from a previous ninja loan financial definition of ninja loan period. When you add up all these direct costs, you get the Cost Of Goods Sold (COGS), a term used in accounting when preparing the company’s financial statement. From the table you can see that direct materials are the integral part and a significant portion of finished goods. Direct materials – cost of items that form an integral part of the finished product.
Production Costs vs. Manufacturing Costs: What’s the Difference?
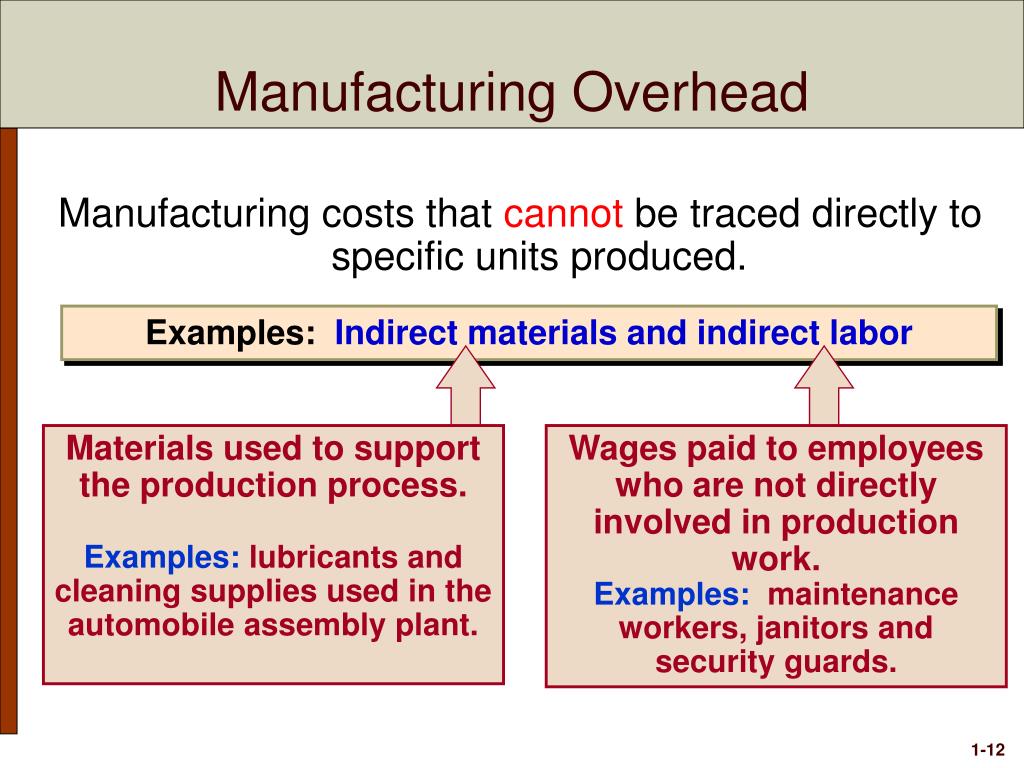
Examples of direct materials for each boat include the hull, engine, transmission, carpet, gauges, seats, windshield, and swim platform. Examples of indirect materials (part of manufacturing overhead) include glue, paint, and screws. Direct labor includes the production workers who assemble the boats and test them before they are shipped out. Indirect labor (part of manufacturing overhead) includes the production supervisors who oversee production for several different boats and product lines. However, if management wants to determine the profitability of a specific product or customer, it is necessary to allocate or assign nonmanufacturing costs to the products and/or customers outside of the financial statements.
Almost half of costs from processes
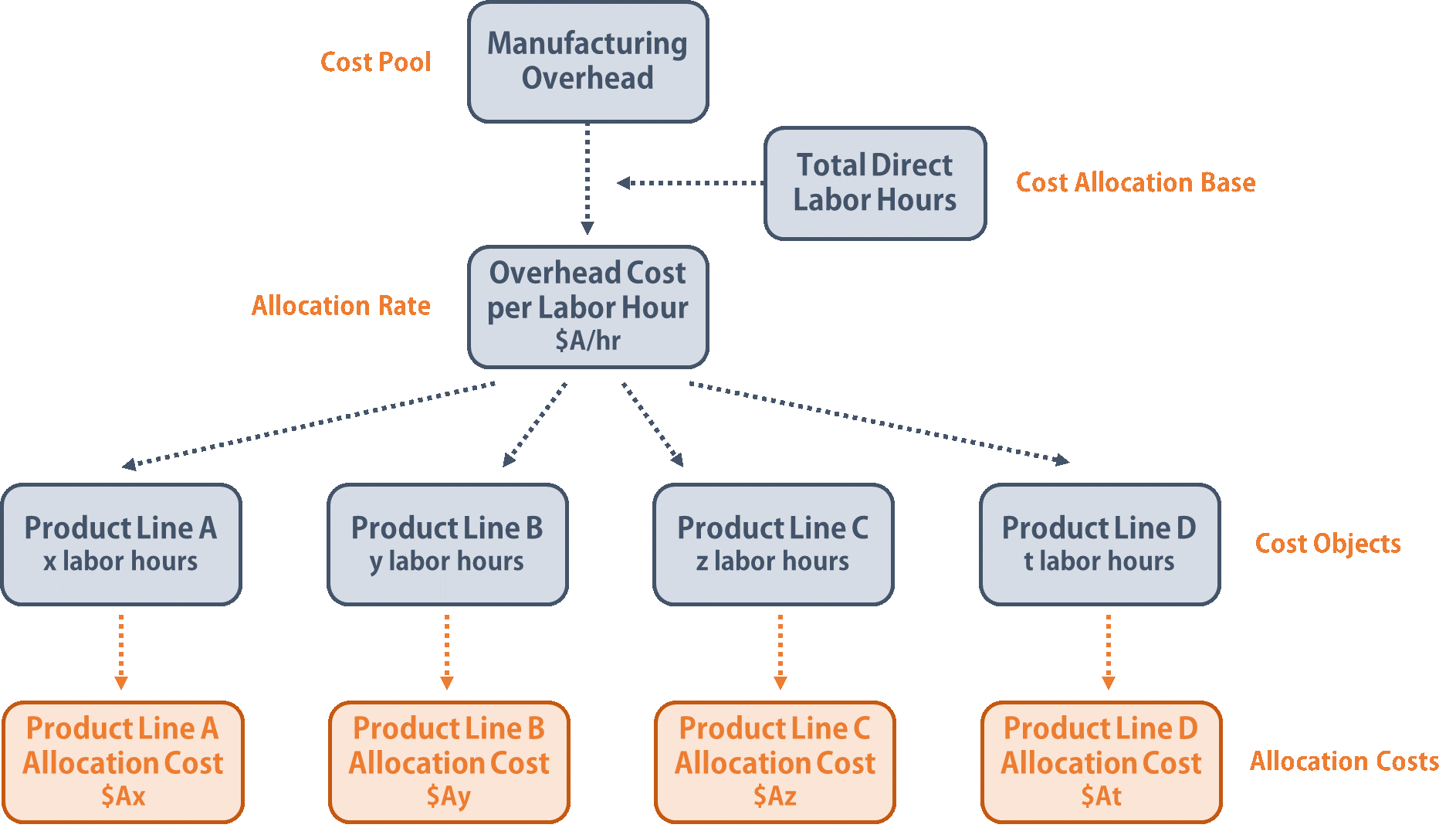
These costs are represented during a period of time and are not calculated into the cost of good sold. Nonmanufacturing costs consist of selling expenses, including marketing and commission expenses and sales salaries and administration expenses, such as office salaries, depreciation and supplies. The purpose of addressing these costs differently as part of a total manufacturing cost formula is based on the fact that they are accounted for differently when structuring the income statement and balance sheet. Even though nonmanufacturing overhead costs are not product costs according to GAAP, these expenses (along with product costs and profit) must be covered by the selling prices of a company’s products. In other words, selling prices must be large enough to cover SG&A expenses, interest expense, manufacturing overhead, direct labor, direct materials, and profit. All manufacturing costs that are easily traceable to a product are classified as either direct materials or direct labor.
Manufacturing and Nonmanufacturing Costs
- They are impacted by different factors and thus their appropriate categorization is important.
- Direct materials are raw materials that become an integral part of the finished goods.
- Let’s go through all the steps for calculating total manufacturing costs.
- For instance, in our example of Friends Company, the company purchases metal parts (raw material) to produce valves.
- Costs that are not related to the production of goods are called nonmanufacturing costs23; they are also referred to as period costs24.
By calculating manufacturing costs, companies can clearly understand the true cost of making a product. Based on this information, the company’s management can add a markup to determine competitive selling prices for their products. Indirect manufacturing costs include all other expenses incurred in manufacturing a product except direct expenses. Direct costs – those that can be traced directly to a particular object of costing such as a particular product, department, or branch.
What about the office rent for the vice president of manufacturing? Therefore, businesses typically establish and adhere to their own criteria. Variable costs – vary in total in proportion to changes in activity. Examples include direct materials, direct labor, and sales commission based on sales. Period costs – are not inventoriable and are charged against revenue immediately. Period costs include non-manufacturing costs, i.e. selling expenses and administrative expenses.
Though most of these costs are self-evident, indirect material costs are unique because these costs are not essential to the physical production of the product. Factory overhead – also called manufacturing overhead, refers to all costs other than direct materials and direct labor spent in the production of finished goods. These costs are reported on a company’s income statement below the cost of goods sold, and are usually charged to expense as incurred.
Phản hồi gần đây